Greenhouse Gas Reporting Methodology
Standard
- Cornell is a signatory of the nonprofit organization Second Nature’s Carbon Commitment. Our Carbon Neutrality Goal is part of the commitment.
- For the baseline greenhouse gas (GHG) inventory, Cornell is using Second Nature’s GHG Protocol Methodology shared by higher education, which is based on the World Resources Institute's GHG Protocol. The GHG Protocol is the global GHG accounting standard for companies and organizations. It is designed to help identify and inform strategic actions an entity can undertake with the greatest impact on emission reductions rather than to create a comprehensive footprint.
- Cornell reports data into a tool called SIMAP (Sustainability Indicator Management & Analysis Platform) for GHG accounting. SIMAP is an online carbon and nitrogen footprint tracking tool designed specifically for organizations with a campus setting and uses The GHG Protocol.
- The annual GHG Inventory report is peer-reviewed by Second Nature.
Boundaries for the Baseline GHG Inventory
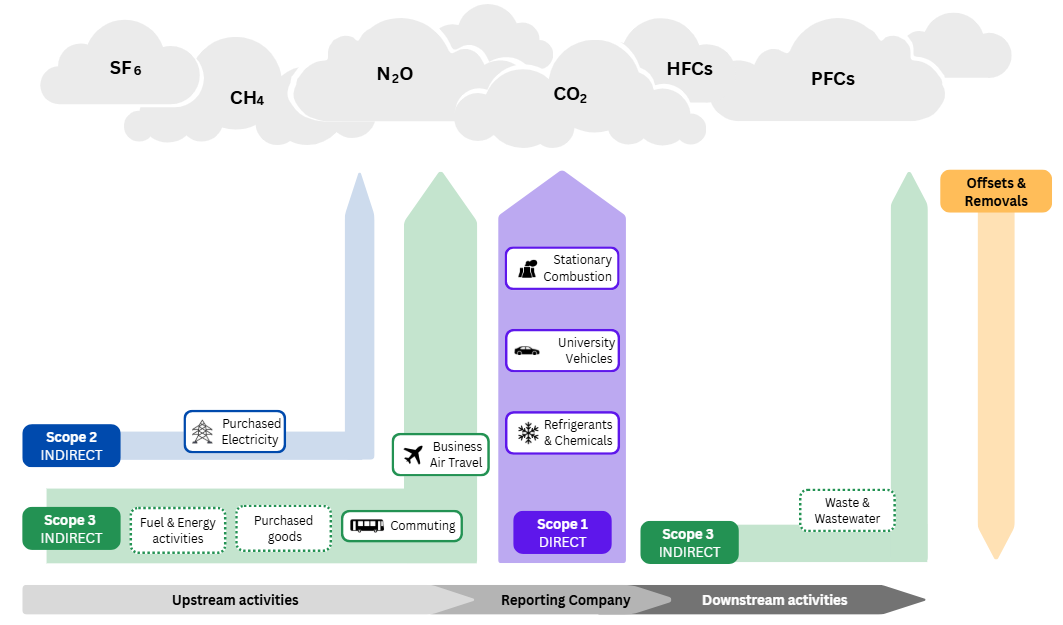
- Emissions from the main six greenhouse gases are inventoried – carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6).
- Emissions of all gases are converted to metric tons of CO2 equivalent (MTCO2e) based on their relative global warming potential on a 100-year time frame.
- The inventory covers the Ithaca, NY campus only.
- The University uses the operational control approach to identify campus boundaries; leased assets are not included.
- Cornell reports Scope 2 emissions using the market-based method.
- Cornell’s baseline year for measuring progress is Fiscal Year 2008, and accounting years are fiscal years.
Included Scopes and Categories for GHG Baseline Inventory
The choice of included scopes is in accordance with our Carbon Neutrality goal and Second Nature’s requirements for the Carbon Commitment.
Data Collection
Cornell’s Greenhouse Gas Inventory is based on the current, most accurate data available for each category. For Scope 1 and 2, the accuracy is high, and the calculation of the emissions is based on annual quantities of purchased gas, fuel, chemicals and electricity. For Scope 3 emissions, calculations are estimates based on various information from spend data to surveys.
We are always attempting to improve the data quality, which sometimes could result in changes in emission calculations. These changes will always go towards higher accuracy.
Emission Factors
In general, Cornell uses emissions factors provided by SIMAP, the calculation tool we use for our Greenhouse Gas reporting. If we have access to more accurate emissions factors for a category, we will use that. SIMAP reviews and updates the emissions factors in their database annually. Each year’s version includes the most up to date emissions factors available. Now and then, these updates will cause substantial changes to the calculated emissions.